Useful Links
What are Incoterms
The term, Incoterms, is an abbreviation for International Commercial Terms. They are a set of rules which define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods under sales contracts for domestic and international trade. They are published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) and are widely used in international commercial transactions. The first Incoterms were issued in 1936. The most recent version of Incoterms, Incoterms 2010, were launched in September 2010 and became effective January 1, 2011.
| EXW | FCA | FAS | FOB | CFR | CIF | CPT | CIP | DAT | DAP | DDP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charge/Fees | EX Works | Free Carrier | Free Alongside Ship | Free On Board | Cost & Freight | Cost Insurance & Freight | Carriage Paid To | Carriage Insurance Paid To | Delivered at Terminal | Delivered at Place | Delivered Duty Paid |
| Packaging | Buyer or Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Loading Charges | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Delivery to Port/Place | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Export Duty & Taxes | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Origin Terminal Charges | Buyer | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Loading on Carriage | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Carriage Charges | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Carriage Charges | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Insurance | Seller | Seller | |||||||||
| Destination Terminal Charges | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller |
| Delivery to Destination | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller | Seller |
| Import Duty & Taxes | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Seller |
ExWorks (EXW)
the seller fulfils his obligations by having the goods available for the buyer to pick up at his premises or another named place (i.e. factory, warehouse, etc.). Buyer bears all risk and costs starting when he picks up the products at the seller's location until the products are delivered to his location. Seller has no obligation to load the goods or clear them for export.
Free Carrier (FCA)
the seller delivers the goods export cleared to the carrier stipulated by the buyer or another party authorized to pick up goods at the seller's premises or another named place. Buyer assumes all risks and costs associated with delivery of goods to final destination including transportation after delivery to carrier and any customs fees to import the product into a foreign country.
Carriage Paid to (CPT)
seller clears the goods for export and delivers them to the carrier or another person stipulated by the seller at a named place of shipment. Seller is responsible for the transportation costs associated with delivering goods to the named place of destination but is not responsible for procuring insurance.
Carriage and Insurance Paid To (CIP)
seller clears the goods for export and delivers them to the carrier or another person stipulated by the seller at a named place of shipment. Seller is responsible for the transportation costs associated with delivering goods and procuring minimum insurance coverage to the named place of destination.
Delivered at Terminal (DAT)
seller clears the goods for export and bears all risks and costs associated with delivering the goods and unloading them at the terminal at the named port or place of destination. Buyer is responsible for all costs and risks from this point forward including clearing the goods for import at the named country of destination.
Delivered at Place (DAP)
seller clears the goods for export and bears all risks and costs associated with delivering the goods to the named place of destination not unloaded. Buyer is responsible for all costs and risks associated with unloading the goods and clearing customs to import the goods into the named country of destination.
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP)
seller bears all risks and costs associated with delivering the goods to the named place of destination ready for unloading and cleared for import.
Free Alongside Ship (FAS)
seller clears the goods for export and delivers them when they are placed alongside the vessel at the named port of shipment. Buyer assumes all risks/costs for goods from this point forward.
Free on Board (FOB)
seller clears the goods for export and delivers them when they are onboard the vessel at the named port of shipment. Buyer assumes all risks/cost for goods from this moment forward.
Cost and Freight (CFR)
seller clears the goods for export and delivers them when they are onboard the vessel at the port of shipment. Seller bears the cost of freight to the named port of destination. Buyer assumes all risks for goods from the time goods have been delivered on board the vessel at the port of shipment.
Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF)
seller clears the goods for export and delivers them when they are onboard the vessel at the port of shipment. Seller bears the cost of freight and insurance to the named port of destination. Seller's insurance requirement is only for minimum cover. Buyer is responsible for all costs associated with unloading the goods at the named port of destination and clearing goods for import. Risk passes from seller to buyer once the goods are onboard the vessel at the port of shipment.
A
AA - Always Afloat
AAAA - Always Accessible Always Afloat
AARA - Amsterdam-Antwerp-Rotterdam Area
ABT - Aboutt
ADCOM - Address Commission
AFSPS - Arrival First Sea Pilot Station (Norway)
AFFREIGHTMENT - The hiring of a ship in whole or part
AFT - At or towards the stern or rear of a ship
AGW - All Going Well
AHL - Australian Hold Ladders
ANTHAM - Antwerp-Hamburg Range
APS - Arrival Pilot Station
ARAG - Amsterdam-Rotterdam--Antwerp-Ghent Range
A/S - Alongside
ATDNSHINC - Any Time Day or Night Sundays and Holidays Included
ATUTC - Actual Times Used to Count
B
BAF - Bunker Adjustment Factor. A Fuel Surcharge expressed as percentage added or subtracted from the freight amount reflecting the movement in the market place price for bunkers.
BALLAST - Heavy weight, often sea water, necessary for the stability and safety of a ship which is not carying cargo.
BAREBOAT CHTR - Bareboat Charter - Owners lease a specific ship and control its technical management and commercial operations only
BBB - Before Breaking Bulk
BDI - Both Dates Inclusive
BENDS - Both Ends (Load & Discharge Ports)
BI - Both Inclusive
BIMCO - The Baltic and International Maritime Council
BL (1) - Bale
BL (2) - (Bill of Lading) A document signed by the carrier which acts as a receipt and evidence of title to the cargo.
BM - Beam
BEAM - The maximum breadth of a ship
BOB - Bunker on Board
BOFFER - Best Offer
BROB - Bunkers Remaining on Board
BSS - Basis
BSS 1/1 - Basis 1 Port to 1 Port
BT - Berth Terms
BUNDLING - This is the assembly of pieces of cargo, secured into one manageable unit. This is a very flexible description, a rule of thumb is to present cargo at a size easily handled by a large (20 tonne) fork lift truck.
BUNKERS - Name given for vessels Fuel and Diesel Oil supplies (Originates from coal bunkers)
BWAD - Brackish Water Arrival Draft
C
CBM - Cubic Meter
CBFT (or CFT) - Cubic Feet
CFR (or C&F) - Cost and Freight
CHOPT - Charterers Option
CHTRS - Charterers
CIF - Cost, Insurance & Freight. Seller pays all these costs to a nominated port or place of discharge.
COA - Contract of Affreightment - Owners agree to accept a cost per revenue ton for cargo carried on a specific number of voyages.
COACP - Contract of Affreightment Charter Party
COB - Close of Business
COD - Cash On Delivery
COGSA - Carriage of Goods by Sea Act
CONS - Consumption
COP - Custom Of Port
CP (or C/P) - Charter Party
CPD - Charterers Pay Dues
CPT - Carriage Paid To
CQD - Customary Quick Despatch
CROB - Cargo Remaining on Board
CRN - Crane
CST - Centistoke
CTR - Container Fitted
CVE - Communication / Victuals / Entertainment
D
DAPS - Days all Purposes (Total days for loading & discharging)
DDU - Delivered Duty unpaid.
DDP - Delivered Duty Paid.
DEM - Demurrage
DESP - Despatch
DET - Detention
DHDATSBE - Despatch Half Demurrage on Actual Time Saved Both Ends
DHDWTSBE - Despatch Half Demurrage on Working Time Saved Both Ends
DISCH - Discharge
DK - Deck
DLOSP - Dropping Last Outwards Sea Pilot (Norway)
DO - Dropping Off Last Sea Pilot (Norway)
DOP - Dropping Outward Pilot
DOT - Department of Transport
DNRSAOCLONL - Discountless and Non-Returnable Ship and/or Cargo Lost or Not Lost
DRAFT - Depth to which a ship is immersed in water. The depth varies according to the design of the ship and will be greater or lesser depending not only on the weight of the ship and everything on board, but also on the density of the water in which the ship is lying.
DRK - Derrick
DUNNAGE - Materials of various types, often timber or matting, placed among the cargo for separation, and hence protection from damage, for ventilation and, in the case of certain cargoes, to provide space in which the forks of a lift truck may be inserted.
DWAT (or DWT) - Deadweight. Weight of cargo, stores and water, i.e. the difference between lightship and loaded displacement.
E
EC - East Coast
EIU - Even if Used
ELVENT - Electric Ventilation
ETA - Estimated Time of Arrival
ETC - Estimated Time of Completion
ETD - Estimated Time of Departure
ETS - Estimated Time of Sailing
EXW - Ex Works
F
FAS - Free Alongside Ship. Seller delivers goods to appropriate dock or terminal at port of embarkation and buyer covers costs and risks of loading.
FD - Free of Despatch
FDD - Freight Demurrage Deadfreight
FDIS - Free Discharge
FEU - Forty foot container equivalency unit - Standard 40'Container
FHEX - Fridays/Holidays Excluded
FHINC - Fridays/Holidays Included
FILO - Free In/Liner Out. Seafreight with which the shipper pays load costs and the carrier pays for discharge Free In/Out. Freight booked FIO includes the seafreight, but no loading/discharging costs, i.e. the charterer pays for cost of loading and discharging cargo.
FIOS - Free In/Out Stowed. As per FIO, but includes stowage costs.
FIOT - Free In/Out and Trimmed. As per FIOS but includes trimming - the leveling of bulk cargoes
FIOSLSD - Free In/Out Stowed, Lashed, Secured and Dunnaged. As per FIO, but includes cost of lashing securing and dunnaging cargo to Masters satisfaction.
FIOST - Free In/Out and Trimmed. Charterer pays for cost of loading/discharging cargo, including stowage and trimming.
FIT - Free In Trimmed
FIW - Free In Wagon
FIXING - Chartering a Vessel
FLT - Full Liner Terms - Shipowner pays to load and discharge the cargo
FMC - Federal Maritime Commission - US government agency
FMS - Fathoms - 6 feet
FO (IFO) - Fuel Oil/Intermediate FO
FOB - Free on Board. Seller sees the goods "over the ship's rail" on to the ship which is arranged and paid for by the buyer
FOFFER - Firm Offer
FOG - For Our Guidance
FOQ - Free On Quay
FOR - Free On Rail
FORCE MAJEURE - Clause limiting responsibilities of the charterers, shippers and receivers due to events beyond their control.
FOT - Free On Truck
FOW (1) - First Open Water
FOW (2) - Free On Wharf
FREE OUT - Free of discharge costs to Owners
FWAD - Fresh Water Departure Draft
FYG - For Your Guidance
FYI - For Your Information
G
GA - General Average
GLS - Gearless
GNCN - Gencon - a standard BIMCO charter party form
GN (or GR) - Grain (capacity)
GO - Gas Oil
GRD - Geared
GRT - Gross Registered Tonnage
GSB - Good Safe Berth
GSP - Good Safe Port
GTEE - Guarantee
H
2H - Second Half
HA - Hatch
HDWTS - Half Despatch Working Time Saved
HMS - Heavy Metal Scrap
HO - Hold
HW - High Water
I
ILOHC - In Lieu of Holds Cleaning
IMDG - International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code
IMO - International Maritime Organisation
IND - Indication
INTERMODAL - Carriage of a commodity by different modes of transport, i.e. sea, road, rail and air within a single journey.
ITF - International Transport Federation - international body that regulates crewing of ships
IU - If Used
IUATUTC - If Used, Actual Time Used To Count
IUHATUTC - If Used, Half Actual Time Used To Count
IWL - Institute Warranty Limits
L
LANE METER - A method of measuring the space capacity of Ro/Ro ships whereby each unit of space (Linear Meter) is represented by an area of deck 1.0 meter in length x 2.0 meters in width.
LASH (1) - To hold goods in position by use of Ropes, Wires, Chains or Straps etc.
LASH (2) - Lighter Aboard Ship - a vessel that loads small barges direct from the water
LAT - Latitude
LOA - Length Overall of the vessel
LOW - Last Open Water
LS (or LUMPS) - Lumpsum
LSD - Lashed Secured Dunnaged
LT - Liner Terms
LW - Low Water
LYCN - Laycan (Layday Cancelling Date)
M
MB - Merchant Broker
MDO (DO) - Marine Diesel Oil
MIN/MAX - Minimum/Maximum (cargo quantity)
MOLCHOPT - More or Less Charterers Option
MOLOO - More or Less Owners Option
MT - Metric Tonne (i.e. 1,000 kilos / 2204.6lbs)
M/V - Motor Vessel
N
NAABSA - Not Always Afloat But Safely Aground
NCB - National Cargo Bureau
NESTING - Implies that cargo is presented stacked in the contour of similarly shaped cargo, it may be likened to a stack of plates.
NON-REVERSIBLE - (Detention). If loading completed sooner than expected, then saved days will not be added to discharge time allowed.
NOR - Notice of Readiness
NRT - Net Registered Tonnage
NYPE - New York Produce Exchange
O
OO - Owners Option
OSH - Open Shelter Deck
OWS - Owners
P
PASTUS - Past Us
PC - Period of Charter
PCGO - Part Cargo
PCT - Percent
PDPR - Per Day Pro Rata
PERDIEM - Per Diem - By the Day
PHPD - Per Hatch Per Day
PRATIQUE - License or permission to use a port
R
RCVR - Receivers
REVERSIBLE - (Detention) If loading completed sooner than expected at load port, then days saved can be added to discharge operations.
ROB - Remaining On Board
RT - Revenue Tonne (i.e. 1.0 metric Tonne or 1.0 cubic meter, whichever greater). The overall RT is calculated on a line by line basis of the Packing List using the largest amount. The overall freight liability is calculated on the total RT amount, multiplied by the freight rate.
S
SATPM - Saturday P.M.
SB - Safe Berth
SD (or SID) - Single Decker
SEAFREIGHT - Costs charged for transporting goods over the sea. This does not cover any haulage or loading/discharging costs but the sea transport only.
SELFD - Self Discharging
SF - Stowage factor. Cubic space occupied by one ton (2,240 lbs/1,000 kgs) of cargo.
SHINC - Sundays/Holidays Included
SHEX - Sundays/Holidays Excluded
SKIDS - Are bearers (timber or steel) positioned under cargo to enable fork lift handling at port, and for ease of rigging and lashing on board ship.
SL - Bale (capacity)
SOC - Shipper Owned Container
SOF - Statement Of Facts
SP - Safe Port
SRBL - Signing and Releasing Bill of Lading
SSHEX (or SATSHEX) - Saturdays, Sundays, Holidays Excluded
SSHINC (or SATSHINC) - Saturdays, Sundays, Holidays Included
STABILITY - It is paramount that a vessel is stable in all respects at all times. When cargo is loaded/discharged, the stability is monitored by a computer, which takes into account the weight and position of cargo within the vessel.
STARBOARD - Subject To Enough Merchandise (Availability of Cargo)
STERN - The aft part of a ship
SUB - Subject (to)
SUPERCARGO - Person employed by a ship owner, shipping company, charterer of a ship or shipper of goods to supervise cargo handling operations. Often called a port captain.
SWAD - Salt Water Arrival Draft
SWDD - Salt Water Departure Draft
T
TBC - to be confirmed
TC - Time Charter - Owners agree to hire a particular ship for a set length of time
TEU - Twenty Foot Equivalency Unit - Standard 20' Container
TTL - Total
TW - Tween Decker
U
USC - Unless Sooner Commenced
UU - Unless Used
UUIUATUTC - Unless Used If Used Actual Time Used To Count
V
VPD - Vessel Pays Dues
W
WCCON - Whether Customs Cleared Or Not
WIBON - Whether In Berth Or Not
WIFPON - Whether In Free Pratique or not
WIPON - Whether In Port Or Not
WLTOHC (distance) - Water Line-To-Hatch Coaming
WOG - Without Guarantee
WPD - Weather Permitting Day
WWD - Weather Working Day
WRIC - Wire Rods In Coils
WWR - When, Where Ready
WWWW - Wibon, Wccon, Wifpon, Wipon
Y
YAR - York Antwerp Rules
A
Air bill Same as Air Waybill
Air Cargo Guide
The official scheduling guide for scheduled air freight services, published by the Official Airline Guides (OAG). It contains current Domestic and international cargo flight schedules, including freighter, wide body and combination passenger-cargo flights. Each monthly issue also contains information on air carriers’ special services, airline and aircraft decoding, airport codes, air carrier and freight forwarders directory, customs information, glossary of ULD terms and information, cargo charter airlines, interline air freight agreements, aircraft loading charts and more.
Air Cargo, Inc (ACI)
A ground service corporation jointly owned by several U.S. scheduled airlines. In addition to its airline owners, ACI serves over 50 air freight forwarders and international air carriers as associate participants. One of ACI’s major functions is to facilitate the surface movement of air freight by negotiating and supervising the performance of a nationwide series of contracts under which trucking companies provide both local pickup and delivery service at airport cities and over-the-road truck service to move air freight to and from points not directly served by the airlines. ACI publishes a directory of these trucking services, listing points served in the United States and the applicable pickup and delivery rates. Other services include claims inspection, terminal handling, telemarketing service, group purchasing )equipment, supplies, insurance) and EDI services.
Air Express
Shipments for which the airline provides a guaranteed level of expedited service, such as overnight, at a premium charge. It may be restricted as to package weight and size.
Air Freight Property
other than mail. Express, or passenger baggage tendered to an airline for transportation.
Air Freight Forwarder
A Service organization which serves the dual role of air carrier (usually indirect) and shipper. To the shipper the air freight forwarder is an indirect air carrier because it receives freight under its own tariff, yet does not actually operate the airplanes. The air freight forwarder provides pick-up and delivery service to and from the shippers dock, consolidates shipments into larger units, prepares shipping documentation and tenders shipments to the airlines. To the airlines, the air freight forwarder is a shipper. Ordinarily an air freight forwarder is classed as an indirect air carrier, however, some air freight forwarders operate their own aircraft.
Airline Tariff Publishing Co. (ATPCO)
Publisher of airline industry tariffs setting forth rates and rules applicable to air freight. Tariffs are available on a subscription basis.
Airport Mail Facility (AMF)
A U.S. Postal Service facility located on or adjacent to an airport that is primarily engaged in the dispatch, receipt, and transfer of mail directly with air carriers.
Airport to Airport
Air cargo service from airport of origin to airport of destination, without pick-up and delivery service.
Air Transport Association of America (ATA)
A trade and service organization for U.S. scheduled airlines. In the cargo field, ATA works with the airlines, the Government, and shippers in developing improved standards and techniques in all phases of air cargo. ATA is an authoritative source of information on cargo matters such as air freight packaging practices, automation, data on air freight growth and statistical data on air cargo services.
Air Waybill (Airbill)
A shipping document used by the airlines for air freight. It serves as a contract for carriage and includes carrier conditions of carriage such as limits of liability and claims procedures. The air waybill also contains shipping instructions to the airline, a description of the commodity, and applicable transportation charges. The airline industry has adopted a standard formatted air waybill that accommodates both domestic and international traffic.
Allowable Cabin Load (ACL)
The maximum payload weight that can be carried on an airplane on a specific route segment under a specific set of operation conditions.
Articles of Extraordinary Value (A.E.V.)
Commodities identified as high value items.
Automatic Proof of Delivery (P.O.D.)
Information automatically sent to payer containing name of person who signed for the package with date and time of delivery.
B
Baggage Passenger
Personal property or other passenger articles transported in connection with a journey. Unless otherwise specified, it includes both checked and unchecked baggage.
Baggage Cart
A towed vehicles used for ramp transport of bulk freight, baggage, and mail.
Belly, Pits or Holds
Compartments located beneath the cabin of an aircraft and used for the carriage of cargo and passenger baggage.
Belt Loader
A vehicle equipped with an adjustable height belt conveyor designed for loading/unloading bulk cargo
Bill of lading
A document by which a carrier receipts for goods and contracts to move them. In airfreight, the air waybill serves as the bill of lading and is the contract for carriage.
Bonded Terminal
An airline terminal approved by the U.S. Treasury Department for storage of goods until Customs duties are paid or the goods are otherwise released.
Break Bulk
Disassembling or unpacking a consolidated shipment for delivery or for reconsignment.
Bulk Cargo
Loose cargo, not unitized, not loaded in containers or on pallets.
Bulk Cargo Carts
Mobile units which transfer the bulk cargo from the airplane to the cargo handling terminal or to other airport locations.
Bulk Loaded
Cargo loaded as loose pieces into airplane compartments.
C
Cargo Aircraft
Aircraft for the carriage of cargo only, rather than the combination of passengers and cargo. Cargo aircraft carry palletized or containerized traffic on the main deck and either unitized or bulk cargo on the lower deck. Cargo aircraft are normally equipped with special cargo loading systems on the main deck. Also referred to as freighters or all-cargo aircraft.
Cargo Agent
An agent appointed by an airline to solicit and process international air freight for shipments. Cargo agents are paid commissions by the airline.
Cargo Loader
Mobile equipment with elevation platforms and powered rollers for loading/ unloading ULDs on airplane main decks or lower lobes. It may be “scissor†or “post†design, or a forklift equipped with a non- powered roller platform.
Cartage Agent
AGround service operator who provides pickup and delivery in areas not served directly by air carrier.
Chargeable Weight
The weight of the shipment used in determining air freight charges. The chargeable weight may be the dimensional weight or the actual scale weight of the shipment. See dimensional weight.
Charges Collect
Transportation charges may include pickup and/or delivery and are entered on the air waybill to be collected from the consigned. Equivalent terms are “freight collect†or “charges forward.â€
Charter Service
The temporary hiring of an aircraft, usually on a trip basis, for the movement of cargo or passengers.
Check Digit Number
A single digit of the air waybill number used to insure that the air waybill number is correctly entered into a computer system.
Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB)
Federal agency created by Congress in 1938 to promote the development of the U.S. air transport system, to award air routes, and to regulate passengers fares and cargo rates. Legislation passed by the U.S. Congress in 1978 terminated the CAB, effective January 1, 1985. Many of the CAB functions were transferred to the Department of Transportation (DOT).
Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB)
Federal agency created by Congress in 1938 to promote the development of the U.S. air transport system, to award air routes, and to regulate passengers fares and cargo rates. Legislation passed by the U.S. Congress in 1978 terminated the CAB, effective January 1, 1985. Many of the CAB functions were transferred to the Department of Transportation (DOT).
Collect Charges
The transportation practice under which the receiver of the goods pays charges. See Charges Collect.
Collect on Delivery (COD)
A transportation service under which the purchase price of the goods in collected by the carrier from the receiver at the time of delivery. Payment Is subsequently transmitted to the shipper. Carriers charge a nominal fee for this service. Payment is due upon delivery. There are no credit provisions in COD service.
COMAT
An acronym for “company-owned material.†The airlines own property (Spare parts, station supplies, ticket stock, etc.) carried on the airlines own airplanes.
Combi Airplane
An airplane configured to carry both passengers and unitized cargo on the main deck.
Combination Carriers
Scheduled air carriers who transport both passengers and cargo in passenger configured aircraft, with cargo restricted to the lower deck compartments.
Consignee
The person or firm whose name appears on the air waybill as the party to whom the goods are to be delivered by the carrier.
Consignment
Synonym for shipment. A shipment of one or more pieces of property, accepted by the carrier from one shipper at one time, receipted for in one lot, and moving on one air waybill.
Consignor
The person or firm whose name appears on the air waybill as the party contracting with the carrier for carriage of the goods. Usually the shipper.
Consolidation
A number of separate shipments that have been assembled into one shipment for movement on one air waybill from one location to another.
Consolidator
An entity that provides consolidation services, joining multiple shipments into a single shipment for tender to an air carrier. An Air Freight Forwarder performs the function of a consolidator.
Container
A unit load device (ULD) which interfaces directly with the airplane cargo handling and restraint system. (See Unit Load Device.)
Containerization
The practice or technique of using a boxlike device (containers) in which a number of packages are stored, protected, and handled as a single unit in transit.
Container, Non-structural
A bottomless, rigid shell made of fiberglass, metal or other suitable material used in combination with an airplane pallet and net assembly.
Container Rate
A rate for the transportation of an entire container or ULD at a uniform charge, regardless of the weight of its content, unless a pivot weight is specified (See Pivot Weight)
Container, Structural
A rigid structure that performs the function of a ULD without the use of restraining net.
Contoured ULD
A ULD shaped to fit the airplane envelope to utilize the maximum space available.
Contract Rate
An unpublished rate established by contractual agreement between a carrier and a regular shipper, usually linked to a minimum volume requirement over a specified time period. Contract rates are sometimes a specified percentage discount of published rates.
Convertible Airplane An airplane which can be converted from an all-passenger configuration to an all-cargo configuration or vice-versa, or to various configurations of passengers and cargo.
Coordinated movement
The coordination and preplanning of schedules and air transport services between two or more carriers or shippers, often involving interline agreements and joint rates. Such services may involve the use of all forms of air as well as surface transport.
Courier Attendant
who accompanies cargo shipment(s). Also, attendant such as groom or veterinarian who accompany rare horses or other live animals.
Cube Rule
A tariff basis stating the minimum density on which weight-based charges are to be computer (See Dimensional Weight)
Cubic Capacity
The carrying capacity within an aircraft or container expressed either in cubic feet, cubic inches, cubic centimeters or cubic meters.
Customhouse Broker
A broker who is certified by the U.S. Bureau of Customs to act for importers and other businessmen in handling the sequence of Customs formalities and other details related to the legal importation of goods.
Customs
The designated government authority that regulates the flow of goods to/from a country and collects duties levied by a country on imports and exports. The term also applies to the procedures involved in such collection.
Customs Court
A U.S. Customs Services court based in New York, NY, consisting of three 3-party divisions to which importers may appeal or protest classification and value decisions and certain other actions taken by U.S. Customs Service.
Customs Declaration
A statement, oral or written, attesting to the correctness of description, quantity, value, etc., of merchandise offered for importation into the United States.
CWT Hundredweight (100 lb).
The standard unit used for establishing U.S. domestic cargo rates, other than specified container rates.
D
Dangerous Goods
The United Nation’s official term for Hazardous Materials. Articles or substances which are capable of posing a significant risk to the health or safety of the general public when transported by air and which are classified according to the most current editions of the ICAO Technical Instructions for the Safe Transport of Dangerous Goods by Air and the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations. See Hazardous Materials.
Declared Value for Carriage
The value of goods declared to the carrier by the shipper for the purposes of determining charges of or establishing the limit of the carrier’s liability for loss, damage, or delay. See Valuation Charges.
Declared Value for Customs
The selling price of the contents or the replacement cost if the contents are not for resale. The amount mush be equal to or greater than the declared value.
Deferred Air Freight
Property received for air transportation at a level of service lower than standard service (e.g., space available) and transported at a lower charge than standard air freight.
Deferred Rate
TA rate that is lower than the corresponding standard rates for a comparable shipment. A shipper using a deferred rate agrees to accept a lower level or service in return for the lower rate.
Demurrage
The detention of containers by shippers or receives of freight beyond a specified grace period. The airlines tender carrier owned containers to the customer for loading and unloading of the unit. In the event the container is not returned to the carrier within a specified time (usually 36-48 hours) a charge may be assessed by the carrier for each 24-hour period or fraction there of beyond the allowed time.
Density
Density is weight per unit of volume. Density is computer by dividing a shipments weight by its cubic volume. Generally expressed in pounds per cubic foot in the U.S.
Department of Transportation (DOT)
An executive department of the U.S. Government established by the Department of Transportation Act of 1966 for the purposes of developing national transportation policies. As a result of the Airline Deregulation Act of 1978, the Dot acquired many of the functions of the CAB.
Dimensional Weight (Volume Weight)
A computed weight based on a minimum density requirement. It is used to determine the freight charges for low dense shipments. It is computed by dividing the shipment volume by the minimum density requirement. The Dimensional Weight Rule was developed to insure fair compensation for low-density shipments. When a given shipment falls below the minimum density requirement, dimensional weight rather than actual weight is used to calculate the transportation charged. Minimum density requirements vary from carrier to carrier. Some carriers give discounts for shipments of high-density goods.
Direct Air Carrier
An air carrier that operates airplanes on a scheduled or contract (charter) basis, or both, and provides transportation for a charge. An airline as opposed to a freight forwarder.
Dolly
A piece of equipment used to move containers or pallets around the airport with the aid of a tractor.
Door to Door or Dock to Dock
Transportation of a shipment from the shipper’s premises (factory, store, warehouse, etc.) to the consignee’s premises (as opposed to airport to airport).
Duty
The Tax imposed on imports by the Customs authority of a country. Duties are generally based on the value of the goods (ad valorem duties), but may be based on weight or quantity (specific duties) or a combination of value and other factors (compound duties).
E
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
A computerized system for communicating information about a shipment, including tracking and tracing, air waybill information and customs documentation.
Embargo
Temporary refusal to accept traffic for transportation at certain points or in certain routes due to emergencies, limitation of facilities, or other abnormal circumstances.
Exception Ratings
Rates set at a certain percentage above the general commodity rates because they apply to commodities that require special handling, such as live animals, human remains, or automotive vehicles.
Excess Valuation
See Declared Value
Export License
A Government document which permits the “Licensee†to engage in the export of designated goods to certain destinations.
Express
Small parcel shipments for which premium (usually overnight) service is provided.
External Dimensions, ULD
The Extreme outside measurement, including any handles or other protrusions, on a ULD.
External Volume, ULD
The amount of space a ULD occupies in an airplane, calculated using the extreme external dimensions of the unit.
F
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA))
Created under the Federal Aviation Act of 1958 as the Federal Aviation Agency and charged with the responsibility of promulgation operational standards and procedures for all classes of aviation in the United States. With the creation of the cabinet level Department of Transportation in 1966 FAA became a unit within the new Department and received the new designation Federal Aviation Administration. The FAA Administrator, however, continues to be a presidential appointee and the FAA remains a separate entity with most of its former functions. In the field of air cargo FAA promulgates certain stress standards, which must be me in the tie down of cargo in flight.
Foreign Trade Zone
A port designated by the Government of a country for duty-free entry of any non-prohibited goods. Merchandise may be stored, displayed, used for manufacturing, etc. within the zone and re-exported without duties being paid. Duties are imposed on the merchandise (or items manufactured from the merchandise) only when the goods pass from the foreign trade zone into an area of the country subject to the Customs authority.
Free Along Side (FAS)
A basis of pricing meaning the price of goods alongside a transport vessel at a specified location. The buyer is responsible for loading the goods onto the transport vessel and pays all the cost of shipping beyond that location.
Free Domicile
A term used in international transportation where the shipper pays all transportation charges and any applicable duties and/or taxes.
Free On Board (FOB)
A pricing term indication that the quoted price includes the cost of loading the goods into transport vessels at the specified place.
Free Trade Zone
See Foreign Trade Zone
Freight
Generally refers to air cargo, but does include air express, mail or passenger baggage.
Freighter
An all-cargo airplane. See Cargo Aircraft
Freight Forwarder
See Air Freight Forwarder
F
General Commodity Rate (GCR)
An air freight rate applicable to all commodities except those for which specific rates have been filed such rates are based on weight and distance and are published for each pair of cities an airline serves.
General Order (GO)
Merchandise not entered within 5 working days after arrival of the carrier and subsequently stored at the risk and expense of the importer.
Gross Weight
Entire weight of a shipment including the weight of containers (tare weight) and packaging material. On an air waybill, the tare weight (when applicable) and shipment weight are listed separately.
F
Hazardous materials (Hazmat)
The U.S. Government official term for Dangerous Goods. Items of freight that are inherently harmful and classified under Title 49, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). Hazardous Materials may only be transported under certain conditions relative to packaging, quantity carried, airplane type, location on board the airplane, etc., and in conformance with applicable rules. Also see Dangerous Goods.
High Capacity Airplane
Equivalent to wide-bodied airplanes. Specifically refers to B747, B767, B777, A300, A330, A340, DC10, MD-11, L-1011, IL-86 & IL-96.
Hold For Pickup
Freight to be held at the carrier’s destination location for pickup by the recipient.
Hub and Spoke System
An airline route pattern that directs traffic from many cities into a central hub designed to connect with other flights to final destinations. They system maximizes fleet utilization by connecting many markets through a central hub with fewer flights than would be required to connect each pair of cities in a point to point system.
I
Igloo
A structural or non-structural container contoured to the dimensions of a standard-body freighter main deck.
Import License
A document required and issued by some national governments authorizing the importation of goods into their individual counties.
In Bond
As applied to air freight coming into the United States, the term “in Bond†refers to a procedure under U.S. Customs rules where the clearance of cargo is postponed until the cargo reaches an inland Customs point rather than subjecting the cargo to clearance procedures at the first arriving U.S. gateway airport where process might be more time consuming. The procedure is so named because the cargo moves under the carrier’s bond (financial liability assured by the carrier) from the gateway airport and remains “In Bond†until Customs releases the cargo at the inland Customs point (airport).
Indirect Air Carrier
Indirect air carriers are those businesses authorized to receive freight from shippers under their own tariff, but who utilize certified air carriers (direct air carriers) to perform the air transportation services. See Air Freight Forwarder.
Interline
The movement of a shipment via two or more carriers. See coordinated Movement and Intermodal Compatibility.
Intermodal
Movement of goods by more than one mode of Transport, i.e. railroad, truck, ship and airplane, in the same ULD, under a singe waybill.
Intermodal Compatibility
The capability to transfer a shipment from one mode of transport to another, as from airplane to highway truck, to railway freight car, to ocean vessel. Certain aircraft can accommodate large types of standard containers commonly used in surface transport.
Intermodal Container
A structural container designed for carriage on airplanes, trucks, rail cars, and ocean vessels and equipped with corner fittings for restraint on a truck chassis and/or for lifting by crane or other loading mechanism.
Internal Fittings
A means of securing cargo inside a container.
Internal Volume, ULD
Maximum available space within the container or pallet net envelope.
International Air Transport Association (IATA)
An international trade and service organization for airlines of more than 100 countries serving international routes. IATA activities on behalf of shippers in international air freight include development of containerization programs, freight handling techniques and, for some airlines, uniform rates and rules.
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO)
The International Aviation Organization of Governments, ICAO is an agency of the United Nations . It was organized to insure orderly worldwide technical development of civil aviation.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO))
A worldwide federation of national standards organizations. “ISO container†denotes a container equipped with standard ISO corner fittings for lifting or for retaining on a truck chassis.
J
Joint Rate
A single through-rate on cargo moving via two or more air carriers or air and surface carriers.
Just in Time (JIT)
The principle of production and inventory control that calls for immediate movement of raw materials, component parts, and work-in-progress. Goods arrive when needed (just in time) for production or use rather than becoming expensive inventory that occupies costly warehouse space.
L
Lay Order
The period during which the imported merchandise may remain at the place or unloading without some action being taken for its disposition, i.e., beyond the 5-day General Order period
Length & Girth
A limitation on shipment size occasionally used by an airline. The equation used to calculate length and girth: Length + (2 x width) + (2 x height). The largest measurement always used as the length in the equation.
Letter of Credit (LC)
A document issued by a bank at the request of the buyer of goods. The LC guarantees payment to the seller given receipt by the bank of certain shipping documents validating the delivery of goods, within a specified time period.
Load Factor, Cargo
The percentage of total available cargo capacity occupied by revenue cargo. It may be computer on the basis of volume, weight, or ULD capability.
Loading Gauge
A rigid framework in the shape of an airplane interior contour for the purpose of checking a pallet load on the ground to ensure it will fit into a particular position in a specific airplane type. Also referred to as a template.
Loose Cargo, Loose Shipments
Air cargo delivered to an airline as separate packages and loaded and unloaded onto airplanes (or ULDs) by airline employees, and then delivered as separate pieces to the consigned. See Bulk Cargo.
Lot Labels
Labels attached to each piece of a multiple lot shipment for identification purposes.
Lower Deck
The compartment below the main deck (also called “lower love,’ ‘Lower hold,’ ‘pit’ or ‘belly’).
Lower Deck Container/Pallet
A ULD shaped to fit the lower deck cargo compartment. These units come in half sizes and full sizes, related to the width across the airplane.
LTL Less Than Truckload
A term used by motor carriers to designate small shipments that are handled as loose pieces as opposed to full truckloads.
M
Main Deck
The deck on which the major portion of the payload is carried.
Main Deck Container/Pallet
A ULD carried on the main deck. These units come in half sizes and full sizes, related to the width across the airplane.
Marks
Information placed on outer surface of shipping containers or packages such as address labels, box specifications, caution, or directional warnings.
Maximum Gross Payload
On a cargo airplane, the maximum weight allowed and available for cargo. It includes the weight of the cargo, containers, pallets, straps and nets.
Maximum Gross Weight, ULD
The maximum allowable combined weight of the ULD and its contents (payload).
Memorandum Tariff
Publications which contain rules and rate information extracted from official tariffs. Memorandum tariffs are published by many carriers and are available from these carriers upon request.
Minimum Charge
The lowest rate applicable on each type of air cargo service no matter how small the shipment.
Minimum Weight
The lowest weight at which a freight rate is applicable (See Weight Break).
N
Negotiated Rate
In the U.S., an agreed rate between an airline and a shipper which is not otherwise provided in the current air freight rate tariff. These rates became legal when airfreight was deregulated in November in 1977.
New Weight
The total weight of a shipment less the weight of containers, pallets, nets or straps.
Neutral Air Waybill
A standard air waybill without identification of issuing carrier.
Nonstructural Container
A unit load device composed of a bottomless rigid shell used in combination with a pallet and net assembly.
O
Oversize Cargo
Unusually large or heavy cargo that will not fit in the cargo areas of standard-body freighters or passenger airplanes. Cargo the exceeds the standard dimensions of common ULDs.
P
Pallet
A platform of standard dimensions on which goods are assembled and secured by nets and straps before being loaded as a unit onto an airplane. It has a flat undersurface to interface with ball, roller, or caster surfaces.
Pallet Net
A webbing or rope that can be secured to the pallet edges for restraining a pallet load. It may be used with a nonstructural container.
Pickup and Delivery (PU&D)
An optional service for the surface transport of shipments from shipper’s dock to origination air terminal and from the air terminal of destination to receiver’s dock. For airfreight, an additional charge is usually assessed. It may be provide by an air freight forwarder, an integrated carrier, or by an independent truck operator either separately or under contract to an airline.
Pivot Weight
For shipments moving at container rates, it is the weight at which an additional charge is incurred for each pound over the picot weight. For shipments moving at bulk rates, the pivot weight is the weight at which it becomes less costly to pay the minimum charge at the higher weight break, than to pay for the actual weight at the lower weight break.
Port of Entry
An officially designated place at which a U.S. Customs officer is assigned with authority to accept entries of merchandise, to collect duties, and to enforce the various provisions of the U.S. Customs laws.
Prepaid Charges
The transportation trade practice under which the shipper pays transportation charges.
Priority Air Freight
Those shipments that have first claim on available air transport capacity, transported at a premium charge.
Proof of Deliver (P.O.D.)
Information provide to payer containing the name of person who signed for the package with the date and time of delivery.
Protective Service
A protective service provided by airlines where shippers arrange to have a shipment under carrier surveillance tat each stage of transit from origin to destination. The service may extend to pickup and delivery and may include armed guard protection. See Signature Service.
R
Restraint System
The system installed in the floor of an airplane compartment that secures the ULD onto the floor to prevent its movement during flight. Also, a net in front of the cargo load to protect the flight crew and/or passengers.
Restricted Articles
An outdated term used to denote Dangerous Goods. These term is no longer used in regulations. See Dangerous Goods and Hazardous Material.
Road Feeder Service (RFS)
Freight service provided by the airlines using motor trucks, generally in conjunction with an air movement.
Roller Ball Transfer
A conveyor system in an airplane or in terminal facilities consisting of various sizes of balls or rollers over which ULDs con be moved.
S
Seat Track
A standardized track on the main-deck of an airplane, designed to accept tie-down fittings. It is typically a continuous track capable of accepting tie-down fittings at any of the regularly spaced intervals provided. May also be referred as a cargo track.
Shell
The superstructure of any container or igloo.
Shipment
One or more pieces of freight being transported under the contracted authority of one air waybill.
Shipper’s Exportation Declaration (SED)
A form required for the export of goods from the U.S., when the value of a single shipment of one commodity is more than $1,500, or when an export license is required.
Shipper’s Letter of Instruction
A form used by a shipper to authorize an airline to issue an air waybill on the shipper’s behalf. The for contains all details of shipment and authorizes the airline to sign the air waybill in the name of the shipper.
Signature Service
A service designed to provide continuous responsibility for the custody of shipments in transit, so named because a signature is required from each person handling the shipment at each stage of its transit form origin to destination.
Small Package Service
A specialized service guaranteeing the delivery of small parcels within specified express time limits, e.g. same day or next day. This traffic is subject to size and weight limitations. Most passenger air carriers also provide this service at airport ticket counters with delivery at destination baggage claim area. Often referred to as counter to counter.
Special Rates
Rates that apply to traffic under special conditions in selected makers. Examples of such rates are container rates, exception ratings, and surface-air rates.
Specific Commodity Rates (SCR)
Rates applicable to certain classes of commodities. Usually these rates are applied to commodities that move in large volume shipments in a given market. Hence, specific commodity rates re usually lower than the general commodity rate between the same pair of cities.
T
Tare Weight
The actual weight of a container or pallet when empty, including all liners and/or fittings.
Tare Weight Allowance
A free weight allowance given to shippers as part of a unitization incentive program for ULDs.
Tariff
A document setting forth applicable rules, rates, and charges for the movement of goods. A tariff sets forth a contract of carriage for the shipper, the consignee, and the carrier. Tariffs are sometimes published by the carriers themselves and by a variety of publishing agencies, such as the Airline Tariff Publishing Company (ATPCO), The Air Cargo Tariff (TACT) and Cargo Rates Services, Inc.
Template
See Loading Gauge
Thermal ULD
A ULD built with insulating walls, doors, floor and roof which retard the rate of heat transmission between eh inside and the outside of the ULD.
Tie-down Strap
A strap which secures a load to the ULD or the airplane restraint system.
Time Definite
Delivery Service standards offered by air freight carriers which permit the customer to select a specific time frame for delivery. These service standards provide schedule patterns based on same day, next day, second or third day delivery needs and may include door-to-door, dock-to-dock or airport to airport service.
Ton
Commonly a short ton (2,00 lb) as compared to a long or gross ton of 2,240 lb.
Ton Mile
The common measurement of transportation productivity. One ton mile means one ton of cargo flown one mile.
Tonne
French spelling of ton used in the air industry to denote a metric ton (1,000 kg or 2,204.6 lb).
Tonne Kilometer
The international or metric version of ton mile. One tonne kilometer means one tonne (metric) flown one kilometer.
Tracking / Tracing
A carriers system of following and recording movement intervals of shipments from origin to destination.
Trailer
A towed vehicle with a roller platform for hauling ULDs between the cargo terminal and the airplane. Trailers range from 10-ft dollies to 40-ft ISO-fitted chassis. The roller platform may be powered or unpowered.
Transit Air Cargo Manifest (TACM)
Procedures under which air cargo imports move through the gateway city to the city of final U.S. Customs destination for the collection of duty and other import processing.
U
Unitization
The practice or technique of consolidation many small pieces of freight into a single unit, usually through the use of aniline ULDs.
Unit Load
A number of pieces of freight or cargo in a single box or container, or on a pallet held in place by a net, strapping, or similar device to make them suitable for transporting, stacking, or storage as a unit. It is also a single large item packaged for transporting, stacking, or storage.
Unit Load Device (ULD)
Term commonly used when referring to containers, pallets and pallet nets. The purpose of the ULD is to enable individual pieces of cargo to be assembled into standardized units to ease the rapid loading and unloading of airplanes and to facilitate the transfer of cargo between airplanes have compatible handling and restraint systems.
V
Valuation Charges
Transportation charges assessed shippers who declare a value of goods higher than the value of the carriers limits of liability. See Declared Value for Carriage.
W
Warsaw Convention
An international multilateral treaty which regulates, in a uniform manner, the conditions of international transportation by air. Among other things, it establishes the international liability of air carriers and establishers the monetary limits for loss, damage, and delay.
Weight and Balance Manual
Specific document for each airplane that controls the type and number of ULDs that can be loaded, their allowable weight and information on alternating loading arrangements.
Weight Break
Weight levels at which the air cargo rate unit decreases as the shipment width increases. Weight breaks normally occur at standard intervals, such as in international shipments 100, 220, 440, 660, 1100, 2200 pounds. Or 45, 100, 200, 300, 500, 1000 kilograms.
Abbreviations and Acronyms
- A. ACL Allowable Cabin Load
- A. AEV Articles of Extraordinary Value
- A. AMF Airport Mail Facility
- A. AOG Aircraft on Ground
- A. NCFF National Committee of Freight Forwarders (UAE)
- A. AWB Air Waybill
- A. B/L Bill of lading
- A. CAD Cash against documents
- A. CBM Cubic meter
- A. CC Freight collect
- A. CIF Cost Insurance and Freight
- A. COD Cash on Delivery
- A. COMAT Company-Owned Material
- A. CUF Cubic foot
- A. CTR Container
- A. CWT Hundredweight
- A. CY Container yard
- A. DGI Dangerous Goods International
- A. DGR Dangerous material
- A. DOT Department of Transportation
- A. EDI Electronic Data Interchange
- A. ETA Estimated Time of Arrival
- A. ETD Estimated time of departure
- A. FAA Federal Aviation Administration
- A. FAS Free Along Side
- A. FCL Full container load
- A. FTK Freight Tonne Kilometer
- A. FOB Free on Board
- A. F/R CTR Flat rack container
- A. GCR General commodity Rates
- A. GMT Greenwich Mean Time
- A. HAZMAT Hazardous Materials
- A. HAWB House airway bill (Forwarder AWB)
- A. H B/L House bill of lading (Forwarder B/L)
- A. IATA International Air Transport Association
- A. ICAO Int’l Civil Aviation Organization
- A. ISO Int’l Organization for Standardization
- A. JIT Just in Time
- A. KG Kilogram
- A. LC Letter of Credit
- A. LCL Less than container load
- A. LTL Less Than Truck Load
- A. MAWB Master airway bill (Airline AWB)
- A. M B/L Master bill of lading (Shipping line B/L)
- A. NES Not elsewhere Specified
- A. NTSB National Transportation Safety board
- A. OAG Official Airline Guide
- A. ORM Other Regulated Material
- A. O/T CTR Open top container
- A. PAX Passenger(s)
- A. PHC Port handling charges
- A. PU&D Pick-up and delivery
- A. PP Freight prepaid
- A. RFS Road Feeder Service
- A. SCR Specific Commodity Rate
- A. SED Shipper’s Export Declaration
- A. TACM Transit Air Cargo Manifest
- A. TACT The Air Cargo Tariff
- A. THC Terminal handling charges
- A. ULD Unit Load Device
- A. UTC Coordinated Universal Time
- A. WAD World Aviation Directory
- A. W/M Weight or Measurment
Resources for Shipping and International Trade Services
Sea Container Specification
High Cube Container
| Equipment | Interior Dimensions | Door Opening | Top Opening | Tare Weight | Cubic Capacity | Payload* |
|
45' High Cube Container |
L: 13.582 m 44' 6 1/2" |
W: 2.347 m 7'8 1/4" |
|
4,110 kg |
85.7 cbm. |
28,390 kg |
|
40' High Cube Container |
L: 12.056 m 39' 6 1/2" |
W: 2.340 m 7'8" |
|
2,900 kg |
76.0 cbm. |
29,600 kg |

Dry Freight Container
| Equipment | Interior Dimensions | Door Opening | Top Opening | Tare Weight | Cubic Capacity | Payload* |
|
20' Dry Freight Container |
L: 5.919 m 19' 5" |
W: 2.286 m 7'6" |
|
1,900 kg |
33.0 cbm. |
22,100 kg |
|
40' Dry Freight Container |
L: 12.051 m 39' 6 1/2" |
W: 2.286 m 7'6" |
|
3,084 kg |
67.3 cbm. |
27,397 kg |

Open Top Container
| Equipment | Interior Dimensions | Door Opening | Top Opening | Tare Weight | Cubic Capacity | Payload* |
|
20' Open Top Container |
L: 5.919 m 19' 5" |
W: 2.286 m 7'6" |
L: 5.425 m 17'9 1/2" |
2,174 kg |
31.6 cbm. |
21,826 kg |
|
40' Open Top Container |
L: 12.043 m 39' 6" |
W: 2.279 m 7'5 1/2" |
L: 11.585 m 38' |
4,300 kg |
64.0 cbm. |
26,181 kg |

High Cube Reefer Container
| Equipment | Interior Dimensions | Door Opening | Top Opening | Tare Weight | Cubic Capacity | Payload* |
|
40' High Cube Reefer Container |
L: 11.557 m 37'11" |
W: 2.286 m 7'6" |
|
4,320 kg |
65.8 cbm. |
28,180 kg |
|
45' High Cube Reefer Container |
L: 13.102 m 42'11 13/16" |
W: 2.467 m 8'1 1/8" |
|
5,200 kg |
75.4 cbm. |
28,350 kg |
|
40' Reefer Container |
L: 11.207 m 36'9" |
W: 2.216 m 7'3" |
|
4,600 kg |
54.9 cbm. |
25,881 kg |

Flat Rack Container
| Equipment | Interior Dimensions | Door Opening | Top Opening | Tare Weight | Cubic Capacity | Payload* |
|
20' Flat Rack Container |
L: 5.702 m 18'8 1/2" |
|
|
2,330 kg |
|
21,670 kg |
|
40' Flat Rack Container |
L: 11.820 m 38'9 1/4" |
|
|
5,260 kg |
|
25,220 kg |
|
40' Collapsible Flat Rack |
L: 12.08 m 39'7 1/2" |
|
|
5,800 kg |
|
29,200 kg |
|
40' Artificial Tweendeck |
L: 12.065 m 39'7" |
|
|
5,400 kg |
|
39,000 kg |

Air Freight – Unit Load Devices
|
|
ID code(IATA) | United States domestic code | Internal Volume | Limiting Internal Dimensions | * Maximum Gross Weight | ** Tare Weight |
 |
AQD,AMD |
M-1 |
21.15 cu m |
229x305x290/229cm |
6,800kg |
340kg |
 |
AQA,AQ6,AMA |
M-1 |
17.24 cu m |
229x305x229cm |
6,800kg |
330kg |
 |
P6P,PMC |
M-1 |
19.80 cu m |
|
MD 6,800kg |
110kg |
 |
P1P,PAG,PAP,PAJ |
M-1 |
17.97cu m |
|
6,800kg |
110kg |
 |
P1P,PAG,PAP,PAJ |
LD-7 |
11.10 cu m |
|
4,626kg |
110kg |
 |
AA2,AAP |
LD-9 |
10.39cu m |
206x302x152cm |
4,626kg |
200kg |
 |
AAU |
LD-29 |
14.50 cu m |
208x302x152cm |
4,626kg |
260kg |
 |
DLF,DQF |
LD-8 |
6.90 cu m |
140x233x152cm |
2,450kg |
128kg |
 |
AVA,AVE,AKE |
LD-3 |
4.47 cu m |
140x147x152cm |
1,587kg |
77kg |
 |
AVC,AVJ,AKC |
LD-1 |
4.84 cu m |
140x147x152cm |
1,587kg |
77kg |

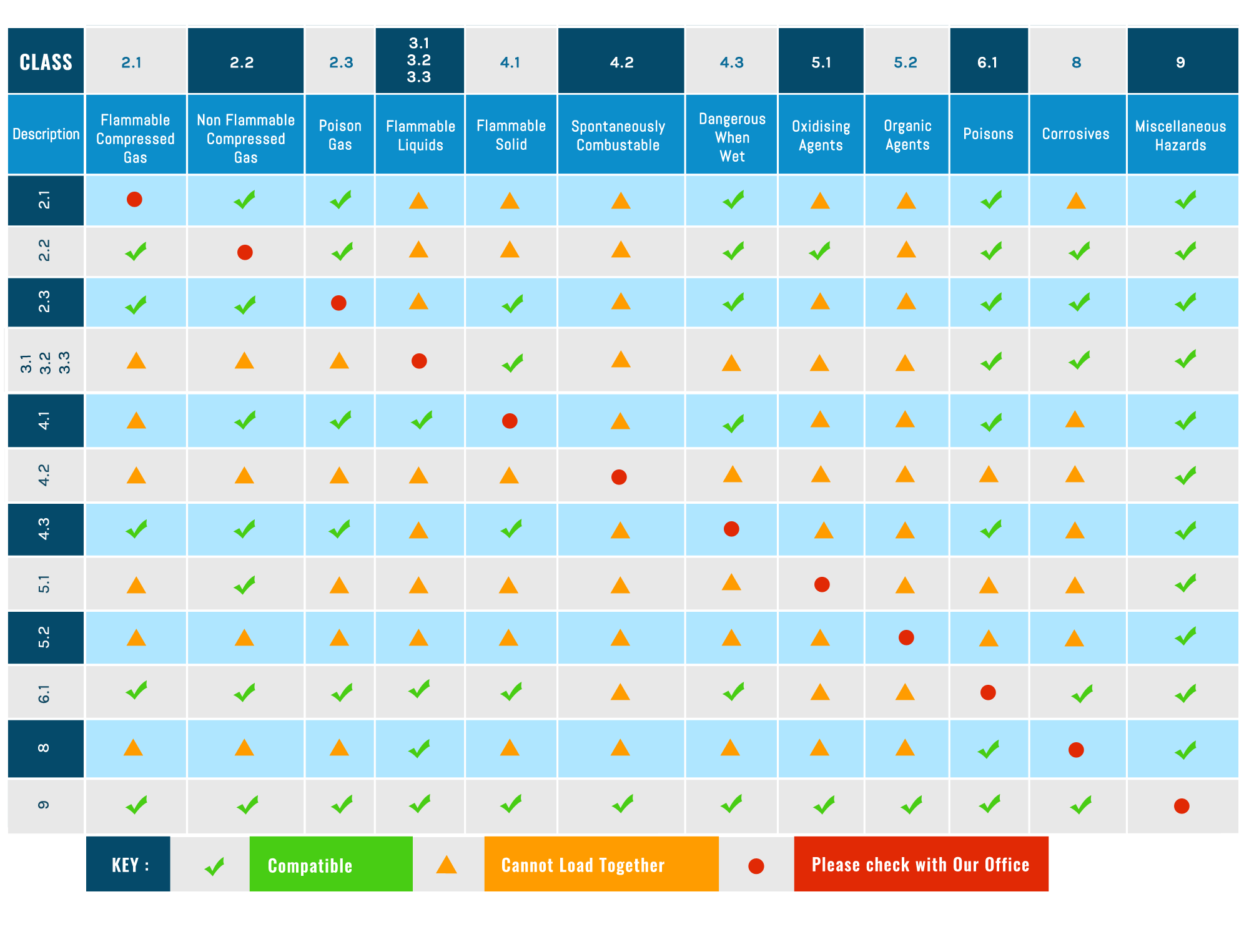
A handy guide for shipping of Hazardous Goods from the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code.
The International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code was developed as a uniform international code for the shipping of hazardous goods by sea covering such matters as packing, container traffic and stowage, with particular reference to the segregation of incompatible substances.
Class 2.1: Flammable Gases:
Gases which are ignitable when in a mixture of 13% or less by volume with air; or have a flammable range with air of at least 12 percentage points regardless of the lower flammable limit.
Class 2.2: Non-flammable, non-toxic gases:
Gases which dilute/ replace the oxygen normally in the atmosphere; or are oxidizing â€" gases which can, by providing oxygen, cause or contribute to the combustion of other material; or gases which are not classed under the other classes.
Class 2.3: toxic gases:
Toxic or corrosive gases know to be hazardous to human health; or are presumed to be toxic or corrosive to humans because they have a LC50 value equal to or less than 5,000 ml/m3 (ppm).
Class 3: Flammable liquids:
Flammable liquids are liquids, mixtures of liquids or liquids containing solids in solution or suspension which give off a flammable vapour at or below 61A°C closed-cup test, normally referred to as the flashpoint. This also includes:
- Liquids offered for transport at temperatures at or above their flashpoint
- Substances transported or offered for transport at high temperatures in a liquid state, which give off a flammable vapour at temperatures equal to or below the maximum transport temperature.
Class 4.1: Flammable solids, self-reactive substances and desensitized explosives:
Solids which, under conditions encountered in transport, can possibly combust or may cause or contribute to fire through friction caused during transport; self-reactive substances (solids and liquids) which are liable to undergo a strongly exothermic reaction; solid desensitised explosives which could explode if not diluted sufficiently.
Class 4.2: Substances liable to spontaneous combustion:
Substances (solids and liquids) which are liable to spontaneous heating under transport conditions, heating up in contact with air or being liable to catch fire.
Class 4.3: Substances which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases:
Substances (solids and liquids) which by interacting with water, are likely to become spontaneously flammable or to give off flammable gases in dangerous quantities.
Class 5.1: Oxidizing substances:
Substances which could cause or contribute to the combustion of other materials. Such substances may be contained in an article.
Class 5.2: Organic peroxides:
Organic peroxides are thermally unstable substances which can undergo exothermic self-accelerating decomposition. In addition, they may have one or more of the following properties:
- burn rapidly;
- cause damage to the eyes;
- be sensitive to impact or friction;
- be liable to explosive decomposition;
- react dangerously with other substances.
Class 6.1: Toxic substances:
These substances can cause death, serious injury or harm human health if swallowed, inhaled or absorbed through skin contact.
Class 8: Corrosive substances:
Substances which by chemical action are likely to cause severe damage when in contact with living tissue or, in the case of leakage, will materially damage or even destroy other goods or the means of transport.
Class 9: Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles:
Substances and articles are substances and articles which, during transport, present a danger not covered by other classes.
Hind Freight Corporate Video Presentation
Our Accreditations







